BMI Calculator – Understand Your Body Weight Clearly

BMI Clarity Index™
A contextual BMI interpretation tool designed for clarity, not judgment.
No personal data is saved or shared.
Enter your height and weight to receive a clear BMI explanation.
This BMI calculator is for informational purposes only and is not a medical diagnosis. Content is reviewed using publicly available medical guidelines (WHO, CDC, NIH).
People search for a BMI calculator because they want answers fast. They want clarity on their weight, their health, and sometimes, peace of mind. I’ve seen it countless times—someone enters their height and weight, clicks calculate, and stares at the number. That moment can be surprisingly emotional. A simple number suddenly carries weight beyond mathematics. People see a label like “normal,” “overweight,” or “obese,” and they freeze. Questions flood in: “Am I okay? Should I worry? Does this mean I’m unhealthy?” These thoughts are natural, and they highlight why BMI continues to spark curiosity and even debate worldwide.
BMI matters because it gives a starting point, not the full story. Hospitals track it. Doctors record it. Public health agencies rely on it. The World Health Organization (WHO) uses BMI to monitor global obesity trends, while the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) uses it to understand population health. Its persistence isn’t accidental—BMI survived because it works on a basic, practical level. Yet it frustrates people. I’ve personally seen athletes labeled “overweight” even when they are fit, and everyday people panic over small changes. Some feel safe when they shouldn’t. This mix of confusion fuels debates, online forums, and even distrust about the number’s value.
I’ve calculated my BMI multiple times, and I can relate to the uncertainty. The number never told the full story for me—it offered context, not conclusions. BMI measures weight relative to height. It does not see muscle. It does not see fat distribution. It cannot measure lifestyle, activity, or medical history. Ignoring these limits causes misunderstanding, but dismissing BMI as useless misses the point entirely. The key is using it as a screening tool—a signal, not a verdict. Health experts emphasize this repeatedly because it works.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) clearly notes that BMI alone cannot diagnose health. Doctors combine it with other measurements: waist size, blood markers, and activity levels all matter. This guide sets expectations. You’ll find a BMI calculator that works instantly. You’ll learn how the number is calculated. You’ll understand what each range means, when it can mislead, and how to use it responsibly. I won’t oversimplify, hide limitations, or scare you. That honesty builds trust. Your BMI does not define you. Numbers are context, not destiny.
What Is BMI? A Simple Explanation That Actually Makes Sense
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It is a number that compares your weight to your height, giving a quick sense of whether your weight falls in a typical range for your size. People often think it tells the whole story, but it does not. BMI does not directly measure body fat. It does not judge fitness or appearance. It simply provides context—a starting point to understand your body relative to height. Using a BMI Calculator can help make this process simple and accurate.
The idea of BMI came from population health research. Years ago, scientists needed a fast, practical way to study weight trends across millions of people. Measuring body fat directly for everyone was impossible. So they created something repeatable and simple. This tool allowed researchers to spot patterns, track obesity rates, and compare populations across countries and age groups. Public health systems could finally plan and respond using real data. The WHO adopted BMI standards, governments implemented them, and the CDC uses them to monitor national health trends. A reliable BMI Calculator follows these standards and gives results you can trust.
BMI works as a screening tool. Like a smoke detector, it alerts you to potential risk without telling you the full story. Doctors rely on tests, medical history, and lifestyle factors to make real health assessments. BMI alone cannot provide a verdict. Yet, many people treat it like a final judgment, causing unnecessary worry or false reassurance. Using a BMI Calculator occasionally, rather than obsessively, keeps it a helpful reference instead of a source of stress.
I’ve seen this firsthand. Friends obsess over a single BMI reading, weighing themselves daily, or constantly recalculating. That behavior adds stress instead of insight. BMI works best when you step back. Look at trends over time rather than fixating on one number. Combine it with how you feel, your activity levels, and your diet. Use it as a conversation starter with your doctor, not as a label. A BMI Calculator can provide neutral reference points that guide, not pressure, decisions.
BMI Calculator – How the Calculation Actually Works
A BMI calculator looks simple, but there’s a precise formula behind it. Two numbers matter: your weight and your height.
Metric formula:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²)
Imperial formula:
BMI = weight (lbs) ÷ height² (in²) × 703
The math never changes; only the inputs do. The metric formula is standard and recommended by the WHO. The imperial formula uses a conversion factor to align with metric standards.

A question I often hear is: Why do we square height? The answer is subtle but important. Taller people are proportionally wider, so weight grows faster than height alone. Squaring height balances the equation and prevents mislabeling tall individuals as overweight or short individuals as underweight. Early researchers tested many formulas, and squaring height produced the most consistent link to health outcomes across populations.
Here’s a practical example:
Switching to imperial units:
This consistency shows the formula’s stability. What does that number mean? It represents weight relative to height. Nothing more, nothing less.
Using the BMI Calculator (Height, Weight, Units)
Everything begins with correct inputs. Height can be entered in meters, centimeters, or feet and inches. Weight can be entered in kilograms or pounds. Units matter. Many people get inaccurate results because they mix units—like entering centimeters as meters or pounds with metric height. Always double-check inputs before hitting calculate.
Once inputs are correct, results appear instantly. Accuracy matters more than speed. This BMI Calculator follows the WHO and CDC formulas with no hidden adjustments. Mobile compatibility and privacy are also important. This BMI Calculator does not store personal data, making it safe to use. After seeing your result, pause and reflect. Numbers are signals, not verdicts. Use the tool as a checkpoint, not a label. Correct inputs produce reliable results. Reliable results support smarter decisions, making BMI genuinely useful.
BMI Categories and Chart – With Real Interpretation
The WHO defines clear BMI categories:
| BMI Range | Category | Risk Interpretation |
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | Possible malnutrition, lower bone density |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal weight | Lower statistical risk at the population level |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight | Increased risk, awareness recommended |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obesity Class I | Higher risk of diabetes and heart disease |
| 35 – 39.9 | Obesity Class II | Significant health risk, medical guidance recommended |
| 40+ | Obesity Class III | Very high risk, close monitoring essential |
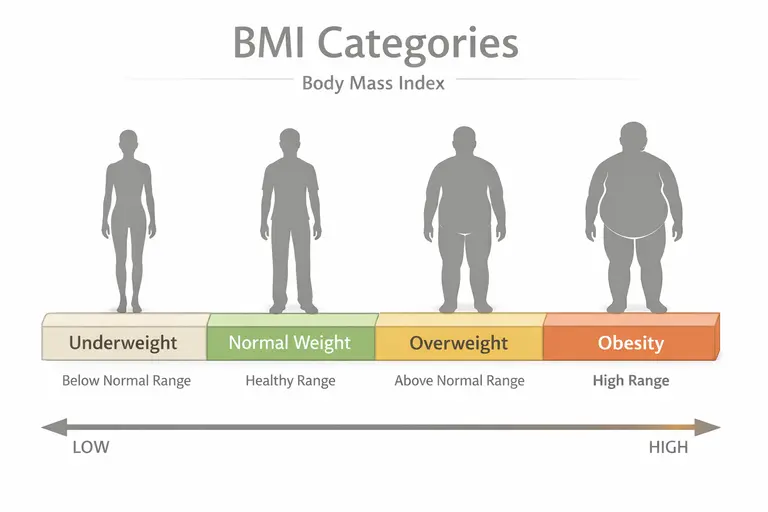
BMI categories describe probabilities, not fate. Individual health depends on age, sex, body composition, lifestyle, and medical history.
Healthy BMI Range – What It Really Means
For most adults, 18.5–24.9 is considered healthy. This range signals lower statistical risk, but does not guarantee perfect health. Factors affecting interpretation:
Healthy BMI is a signal to maintain balance, not a reason to panic or relax. It encourages informed choices and preventive care.
BMI for Different People – Understanding Context Matters
BMI for Men
Men typically carry more muscle, so BMI may overestimate risk. Look at waist size, fitness, and health markers.
BMI for Women
Women carry more body fat naturally. Temporary changes like pregnancy or menstrual cycles affect BMI. Combine BMI with lifestyle habits for a complete picture.
BMI for Teenagers
Use percentiles, not adult ranges. Teens grow rapidly, so a number that seems high may be normal.
BMI for Athletes
High muscle mass may classify athletes as overweight or obese. Combine BMI with body fat percentage and performance metrics.

Limitations of BMI
Despite limitations, BMI remains simple, scalable, and widely recommended. Used wisely, it informs decisions.
BMI vs Other Health Metrics
BMI provides trends; other metrics provide context. Together, they give a fuller picture.
How to Use Your BMI Result Wisely
Common BMI Myths
Understanding myths reduces unnecessary worry and misuse.
Is BMI Accurate? What Science Says
FAQs About the BMI Calculator
Content is reviewed using publicly available medical guidelines (WHO, CDC, NIH).
Final Thoughts About the BMI Calculator

BMI gives information, not judgment. Use it wisely, track trends, and combine it with lifestyle habits and professional guidance. Numbers are context, not destiny. A BMI Calculator can motivate awareness, reflection, and informed health decisions. A “high” or “low” BMI does not predict your future alone. It highlights areas to watch, not areas to fear. Health decisions grow from knowledge, not labels. A BMI Calculator can start conversations with doctors or trainers, and encourage small, consistent improvements. It supports awareness without creating anxiety.
Trust your judgment alongside the tool. Understand what the number truly represents and respect your body’s uniqueness. Approach BMI as a helpful signal, not a final score. Using it thoughtfully gives insight, context, and control over your health. BMI is one piece of a bigger health picture. When combined with lifestyle, monitoring, and professional guidance, it becomes meaningful. Keep perspective, stay informed, and let BMI work for you—not against you. Understanding, context, and calm reflection make it a truly valuable health tool.
Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for medical advice.
